Combining Rigid and Flexible Materials with PolyJet Overmoulding
Create unique, complex geometries with overmoulds by leveraging PolyJet 3D printing

What is an Overmould?
What do you do when you need a part made from two or more materials at the same time. Most commonly, these parts have a rigid section and a flexible section. The rigid section is called the substrate and the flexible section is called the overmould. A common example of an overmould/overmoulded part is your toothbrush! The white, rigid part is the substrate, and the blue, flexible part is the overmould.
Why PolyJet?
Polyjet is the only 3D printing technology we offer that can produce prototypes of overmoulded parts. PolyJet works by dividing the part into voxels, or 3D pixels. It then assigns a material and durometer to each voxel. The machine is loaded with both rigid and flexible material. As the print head moves across the bed, it deposits droplets of material. For 30 Shore A parts, it deposits only flexible resin; for rigid parts, it deposits only rigid resin. For any hardness, or durometer, in between, the print head deposits a mixture of flexible and rigid droplets in a ratio appropriate to the desired hardness. The image below shows what a voxel of 60 Shore A material looks like. Each dot represents a droplet of resin. The white, or primary material, is rigid, and the black, or secondary material, is flexible. The droplets of resin are then instantly cured by a UV lamp.

Because the PolyJet machine can pick and choose what material it deposits where, it’s uniquely able to use multiple durometers and colours on the same part. Most commonly, this takes the form of a rigid substrate with a flexible overmould, but it could also be two flexible materials or two rigid materials.
Material Options
Below are the material options for PolyJet. The three available colours are black, white, and clear. For each material there is a range of durometers, or hardness. All materials fall under the Shore A hardness scale and range from 30 to 95. The durometer scale isn’t hard to figure out: the higher the number, the more rigid the material.
|
Colour |
Black, White, Clear |
|
Durometer |
30A, 40A, 50A, 60A, 70A, 85A, 95A, Rigid |
Note: The softest durometer available for White is 50A.

When choosing colour and durometer, there are some limitations on what combinations we can build. The table below shows the available combinations. Each row represents an available machine configuration. This example part, featuring a Rigid White body with 50A Black buttons would utilize Option 4. However, you would not be able to select a Rigid Black body with 50A White buttons because we don’t have a machine set up with Rigid Black and Flex White. If you’ve accidentally chosen a configuration, we’re not able to accommodate, we’ll let you know and let you choose an alternative before we start building anything.
|
Option 1 |
Rigid White |
Rigid Clear |
Flex Clear |
Flex White |
|
Option 2 |
Rigid White |
Rigid Black |
Flex Black |
|
Configuring Your PolyJet Overmould Quote: Set Up the CAD Model
PolyJet overmould quote requests are a bit different than quoting for any other type of 3D printing. First, we need a .STEP or .STP file of the assembly. In that file, the substrate and the overmould must each have their own solid body. This way, the machine will know what material goes where. Each solid body will be assigned a colour and durometer, more on that later.

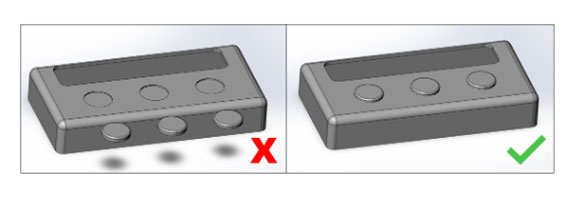
We also require that the file represent the part as you’d like to have it printed. The below image on the left would not work, because it would result in the three buttons being built separate from the main housing. The file on the right is correct because the buttons are in the location in which we want them to build.
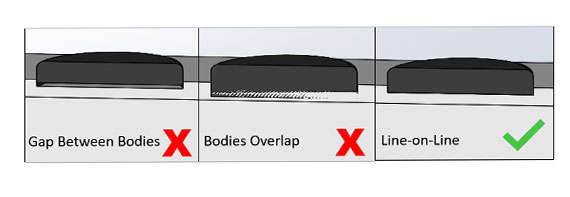
Finally, we also want the various bodies to mate line-on-line. This means there is no gap between the two bodies. If there is a gap, the machine will try to put support matrix between the two bodies. Since the support matrix is designed to be removed, its inclusion makes it easier for the two bodies to separate once the part has built. We also don’t want the bodies to overlap. If the bodies overlap, the machine will try to draw twice in the same area which can cause the build to crash.
Configuring Your PolyJet Overmould Quote: Set Up the Quote
Now that you’ve got your file ready, it’s time to upload! Once the file’s been uploaded, select “Digital OverMould” from the material drop down.
In addition to material selection, we’ll also need to know the colour and durometer for each body in the file. Use the Special Instructions area to provide this information. If you have a formal drawing, that’s great, but even a simple screenshot with arrows will work for us. We prefer a visual indication of colour and durometer because it minimises the opportunity for miscommunication; a picture speaks 1000 words. Below is an example of how to communicate colour and durometer.

Lastly, submit your quote for review by clicking the orange “Request for Quote” button. This sends the quote to our team for review. We’ll review the requested material combination and analyse the parts for any other build concerns. Once we’re done, you’ll get an email notifying you that your quote is complete.
Additional Resources
If you need further assistance, you can reach a member of our applications engineering department in a number of ways:
- Talk to your account manager about setting up a design review.
- Set up a design review with an applications engineer directly using the link in the manufacturing analysis.
- Email customerservice@protolabs.co.uk.
- Call +44 (0) 1952 683047.

If you have any issues getting your guide, click here to download.






