No matter the project, application, or part you are working on, there is one common theme on all product designers' and developers' minds: Speed. How fast can I get a quote? How fast can I get my parts? What is the best way to streamline the process upfront so I can get to market before my competitors?
In this post, we break down how the digital manufacturing method for CNC machining ensures speed, highlighting some of the newest technologies that are helping enable it and offering tips on selecting the right supplier to help get you from design to product-in-hand fast.

The Digital Machine Shop
Technology-enabled digital manufacturers are dramatically different from traditional machine shops. While the traditional shops still rely on manual machine tools, making them more labor intensive, digital manufacturers embrace automation. At Protolabs, our proprietary technology turns CAD models into machined parts in as fast as a single day. The reduction in necessary labor also enables digital manufacturers to operate at a larger-scale capacity, which it turns allows more parts to be produced on a quicker turn, ensuring that parts are shipped rapidly, on-time, and on-budget.
Let’s take a step back. Before receiving your parts, you need to place an order. And, to do that, you must first request a quote. Technology enables an infinite capacity operating model, which allows manufacturers to guarantee consistent lead times, risk reduction capabilities, and reliable pricing. All of this combines to provide a fast and streamlined quoting process, compared to finite operations where you often get varied lead times and no quotes (or quotes that take a long time to get).
Additionally, digital manufacturing supports an automated quoting process, like our web-based system with design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback. The system identifies features that are challenging to machine, upfront, before any production begins, allowing for modifications early on in the design process and avoiding necessary reworks. All of this saves you time and money. In traditional manufacturing, an experienced machinist may be able to provide similar feedback simply looking at a part, but that process is not scalable, fast, or easily repeatable. With automated quoting, an interactive quote with DFM analysis and pricing can be returned to the product designer or engineer in hours.
Industry 4.0 and The Digital Thread
Starting with the first revolution, which signaled a shift from basic hand-production methods to manufacturing machines and tooling, industrial revolutions are the result of technology changes that spur the next phase of industry and manufacturing. Each new revolution forever changes the face of manufacturing. We’re currently in the fourth revolution, commonly referred to as Industry 4.0. This revolution emphasizes that the way we manufacture today will be forever impacted and changed because of the evolution of technology and the digitization of manufacturing.
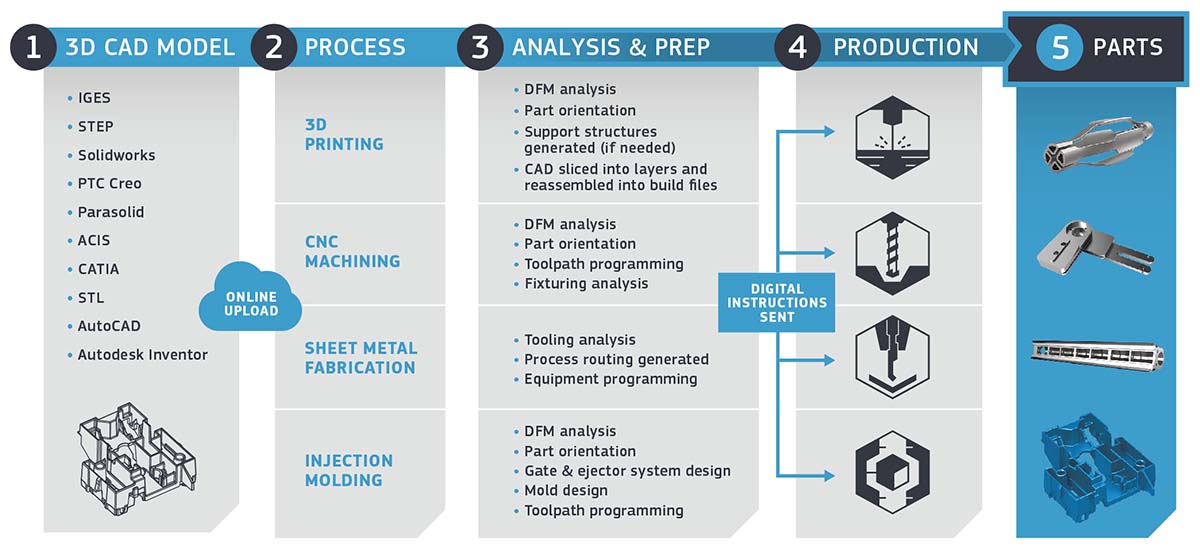
At Protolabs, we talk a lot about our 'digital thread' that has grown out of this fourth revolution. But, what exactly is it? Simply put, it is our technology-enabled, end-to-end automation system. It is the thread that runs through our entire manufacturing process, from the initial CAD model uploaded by a customer, to the final part shipped and in their hands. The software is embodied with design and manufacturing rules extracted from human experts, and used to analyze the geometry of parts that will eventually be manufactured. This automated process allows us to ship machined parts in just one to three days, a speed unheard of in traditional machining.
Embracing digital manufacturing and industry 4.0 also has supply chain impacts. Over the past century, traditional manufacturing has taught us that external threats, such as market demand, and internal challenges affect gross margin and profitability. Digital manufacturing focuses on leveraging technology to minimize the impact of these factors, while creating a manufacturing process that allows for supply chain flexibility and delivers profit.

What's New in Automated Machining?
As innovators in the manufacturing industry, it’s no surprise that companies in this field are on the cutting edge of new automation technologies to streamline and simplify the process. One way digital manufacturers are achieving this is through the use of robots. Robotic automation has found its way into many different areas in manufacturing, including performing tasks like welding, assembly, shipping, handling raw materials, and product packing.
At Protolabs, we recently incorporated an automated block prep robotic system (video on left) into our CNC machining process. This has increased productivity and reduced the amount of labor needed and block prepped compared to our previous process. The automated functionality has enable us to stay consistent with block form, fit, and function, while increasing safety and reducing manual labor. Though implementing this new technology has been a mainly 'behind-the-scenes' effort, it reinforces our digital approach to manufacturing, enabling the speed, consistency, and reliability product designers and engineers look to us for.
5 Things to Look for in a Digital Machining Supplier
So, now that you’ve learned about the efficiencies of digital manufacturing and how this method enables speed, how do you determine the best supplier for your project? Here are five things to consider when looking for a digital machine factory, pulled from our CNC Machining for Prototypes and Low-Volume Production Parts trend report.
- Determining which part volumes any given manufacturer is most competitive with is an important first step—some shops specialize in low-volume and prototype parts, while others are geared toward production runs of tens of thousands and more.
- Don’t be afraid to ask a shop what makes it tick—the most efficient are those that use standardized processes to reduce setup times, tooling costs, and surprises.
- While they come at a cost, standard toolsets often produce the fastest turnaround. Machining centers with a fixed number of tools may need to make those tools perform double-duty, for example, using an end mill to drill a hole.
- Factories that provide DFM upfront allow you to make changes and correct manufacturing difficulties before production begins, saving time and money with reworks.
- Look for a shop that sees the big picture and offers multiple manufacturing options. For example, you might think that 3D printing is the best path to quick delivery of prototype parts. And, this might be the case, but if your part design allows, machining is often a more affordable prototyping option. This also allows you the flexibility to move between manufacturing methods as volume changes.
Embracing digital machining has many benefits, namely speed, moving your part from design to final part in just a couple of days. Beyond this, the automation supports multiple design iterations and accelerated development. This means products get to market fast, and supply chains are better maintained throughout the entire life cycle.





