Automotive 3D Printing
Accelerate automotive product development with 3D printing of rapid prototypes and low-volume production parts for traditional, electric, and autonomous vehicles
Why do Companies in the Automotive Industry use Protolabs?
As industry trends like autonomous driving, on-board connectivity, and hybrid/electric vehicles continue to drive innovation, agility-minded automotive companies are turning to Protolabs to accelerate new product development and get to market faster.
Our diverse 3D printing technologies support customers in the automotive industry by offering:
- design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback on every quote
- quality inspections to validate part geometry and FAI reporting
- ability to 3D print functional prototypes in a variety of material options suitable for testing
- diverse material and process selection to aid in lightweighting components

The above image shows end-use automotive connectors fabricated using Carbon DLS printing.
3D Printing Processes for Automotive Applications

Electric Vehicle Report
Electric and autonomous vehicles make up one of today's hottest growth sectors. And more than ever, car companies are shifting gears and require specialized parts to feed demand. Are you ready? Check out our FREE report to see where the industry is heading and how digital manufacturing can help.
What Materials Work Best for 3D-Printed Automotive Components?
Thermoset Polymers (ABS-like, PC-like, Tough Black). ABS-like all-purpose materials are a solid choice for highly accurate prototypes for “touch and feel” of lightweighted concept parts with minimal thermal design requirements. When thermal requirements are present, leverage advanced PC-Like High-Temp Translucent, which works well for applications such as under-the hood-automotive or electrical components.
Nylons (PA 12, PA 12 Glass-filled, and PA 11). These materials offer high tensile strength and quality surface finish. As workhorse nylons, they are often used to build housings, enclosures, and fixtures, and can work well for snap fits and hinges.
Polypropylene. This true engineering-grade polypropylene can be manufactured using our SLS process. It’s a low weight material, in comparison to other plastics, and it exhibits durability in addition to being both tough and flexible. This material is well suited for functional moving parts with features like snap fits. Excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation make it ideal for automotive and electrical enclosures.
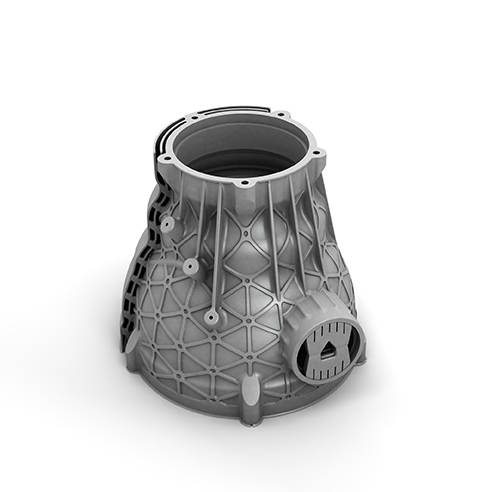
Aluminum. (AlSi10Mg). This material is comparable to a 3000 series alloy that is used in casting and die casting processes. It has good strength-to-weight ratio, high temperature and corrosion resistance, and good fatigue, creep, and rupture strength required in automotive applications.
Ceramic-Filled. Manufactured with Hybrid PhotoSynthesis (HPS) technology, this material is a ceramic-filled composite offering an extremely high stiffness of around 10 GPa and an HDT above 280°C (536°F).
3D Printing Applications for the Automotive Industry
As the shift from traditional to electric and autonomous vehicles unfolds, 3D printing is becoming more and more commonly used, mainly for automotive prototyping and testing. Some of the world’s largest automotive companies utilize 3D printing for its cost-effectiveness during the design iteration phase. End-use production components include everything from custom seating to automotive brackets to fuel nozzles. Other common automotive applications include:
- Sprockets
- Enclosures and housings
- Fan blades
- Gears, latches, and brackets
- Engine parts, manifolds, and heat exchangers
- Hose and wire clips
- Washer fluid and fuel caps
- Fixtures
- Assembly line components
- Plastic dash components
- Customized aftermarket parts
- Lenses and lighting features
- Support for on-board consumer electronics